Why No One Can Dethrone TSMC in the Foundry Business
The semiconductor industry is the backbone of modern technology, and TSMC has firmly established itself as the king of the foundry business due to a combination of technology, strategy & ecosystem.
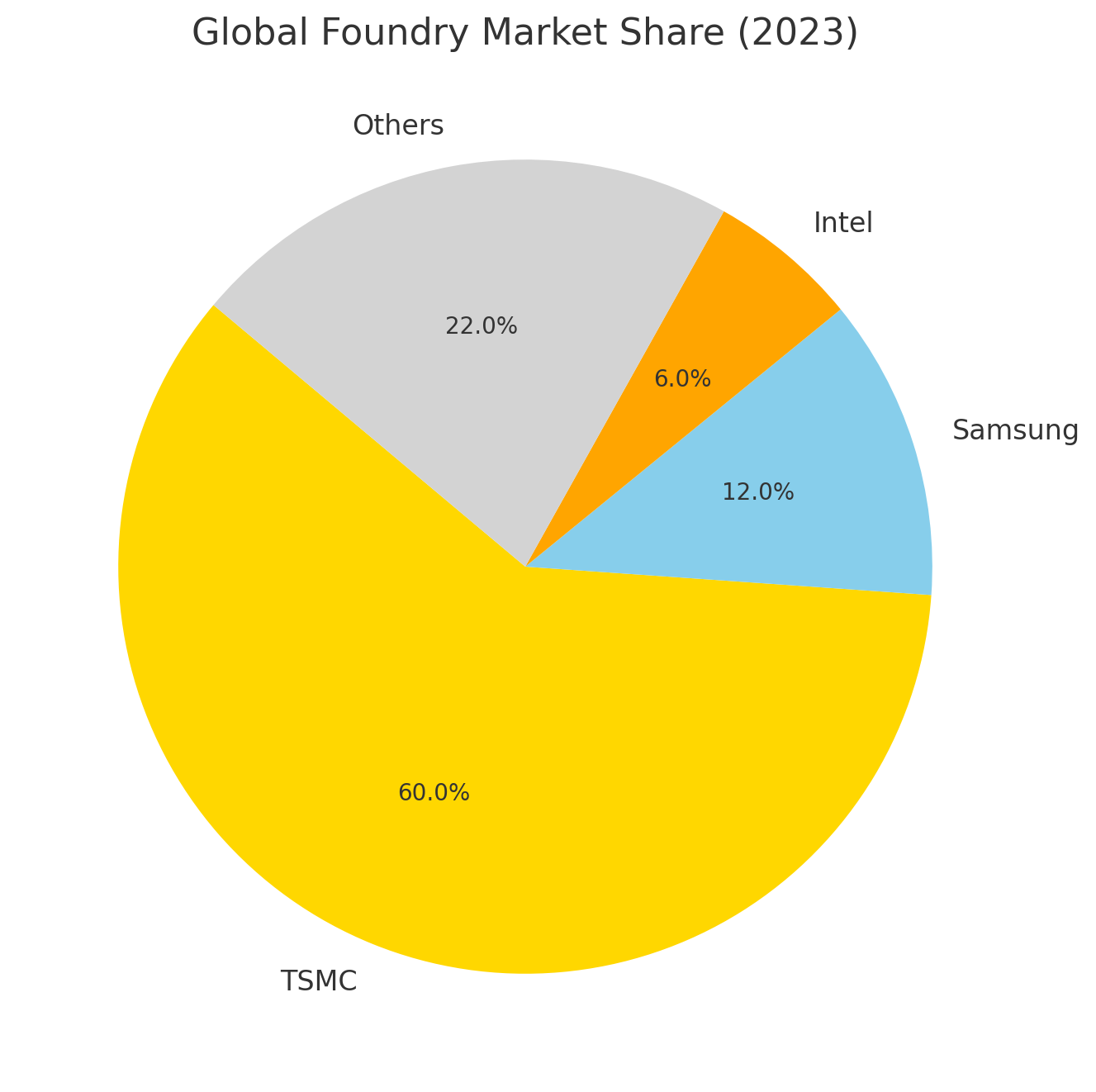
The global foundry market is the arena where technological giants battle for dominance, but one player—TSMC—stands head and shoulders above the rest. Despite fierce competition from Samsung Foundry and Intel, TSMC’s grip on the market remains firm. Why? Let’s break it down through critical pillars that define its unassailable lead. Let’s explore why TSMC continues to hold its throne.
1. Technological Leadership: Relentless innovation
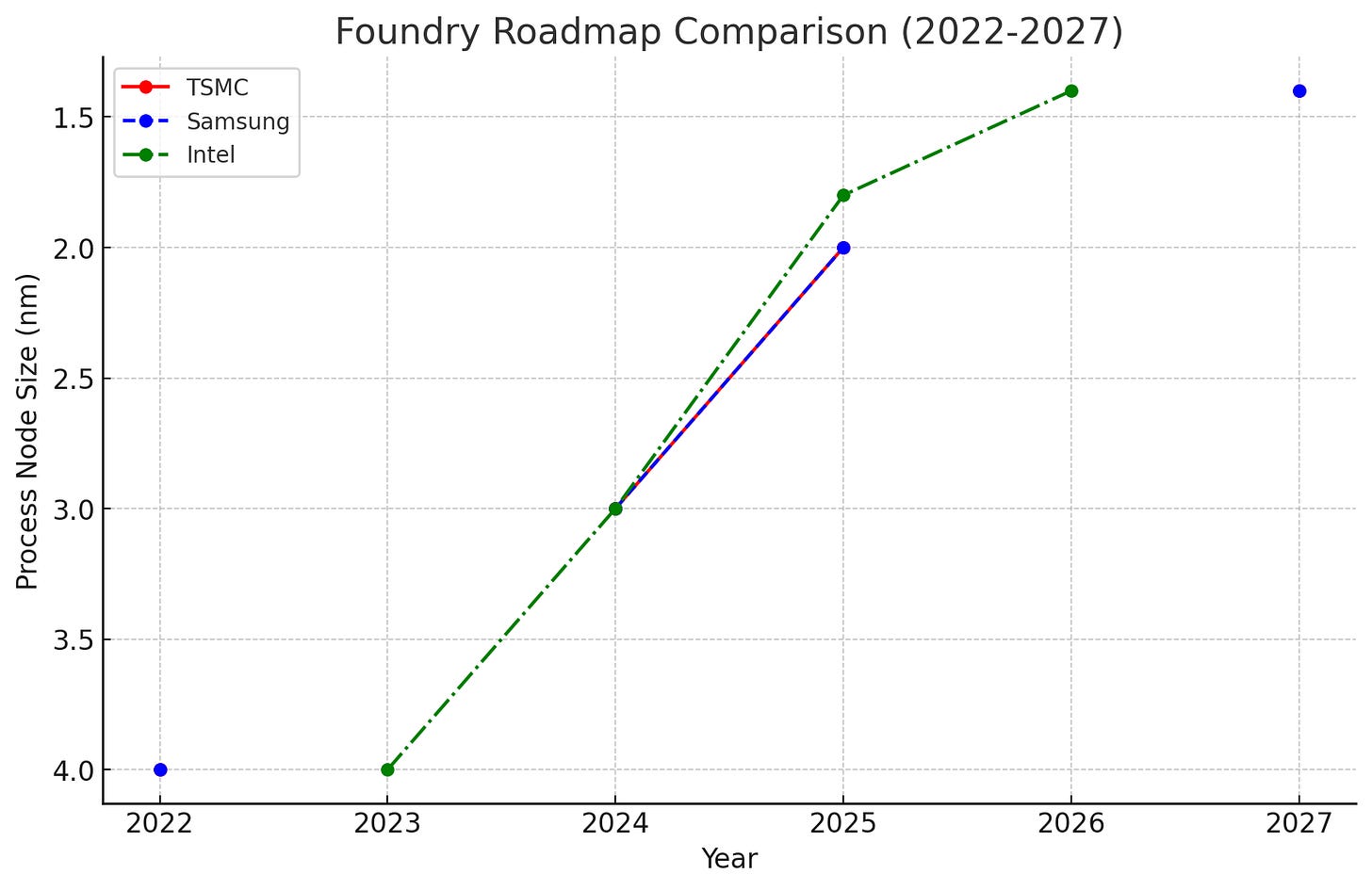
TSMC’s edge lies in its cutting-edge technology, particularly in advanced process nodes. As of 2024, it is the only company capable of mass-producing 3nm chips, with plans to transition to 2nm by 2025. These chips power everything from the latest iPhones to high-performance data centers, making TSMC indispensable to global tech giants like Apple, NVIDIA, and AMD.
The semiconductor foundry business thrives on continuous innovation, and TSMC has perfected the art of delivering new nodes consistently. The company has built an enviable reputation for delivering advanced process nodes—7nm, 5nm, 3nm—on time and at scale, while competitors like Intel and Samsung have struggled to keep pace.
Intel has famously faltered in its execution, delaying key process node rollouts like 7nm, which pushed its entry into the foundry business years behind schedule. Samsung, meanwhile, has encountered yield and scalability issues, especially with its 3nm process.
Key Stat: TSMC accounts for over 60% of the global foundry market revenue, with its nearest competitor, Samsung Foundry, capturing only about 12% as of Q3 2023.
TSMC consistently reinvests profits into new technologies and production capacity, ensuring it stays ahead of the curve. For instance, TSMC’s R&D intensity (R&D expenditure as a percentage of revenue) was over 8% in 2023, compared to 5%-7% for most competitors.
The company’s leadership in packaging technologies, such as CoWoS (Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate) and 3DFabric, has been critical in enabling chiplets and heterogeneous integration, key trends driving next-generation computing.
2a. Strong Customer Ecosystem
TSMC enjoys relationships with nearly every major fabless chip designer, including Apple, Qualcomm, AMD, and NVIDIA. These partnerships are not merely transactional but deeply collaborative, involving co-design efforts to optimize chips for specific applications.
Key Stat: In 2023, Apple alone contributed approximately 25% of TSMC’s revenue, demonstrating the company’s integration into high-margin, high-volume product ecosystems.
But WHY?
2b. Customer Design Enablement: The Secret Sauce
One of TSMC’s greatest, often underappreciated strengths is its customer design enablement ecosystem. The process of taking a chip from idea to silicon requires robust Process Design Kits (PDKs), IP porting, and seamless design support—a domain where TSMC excels.
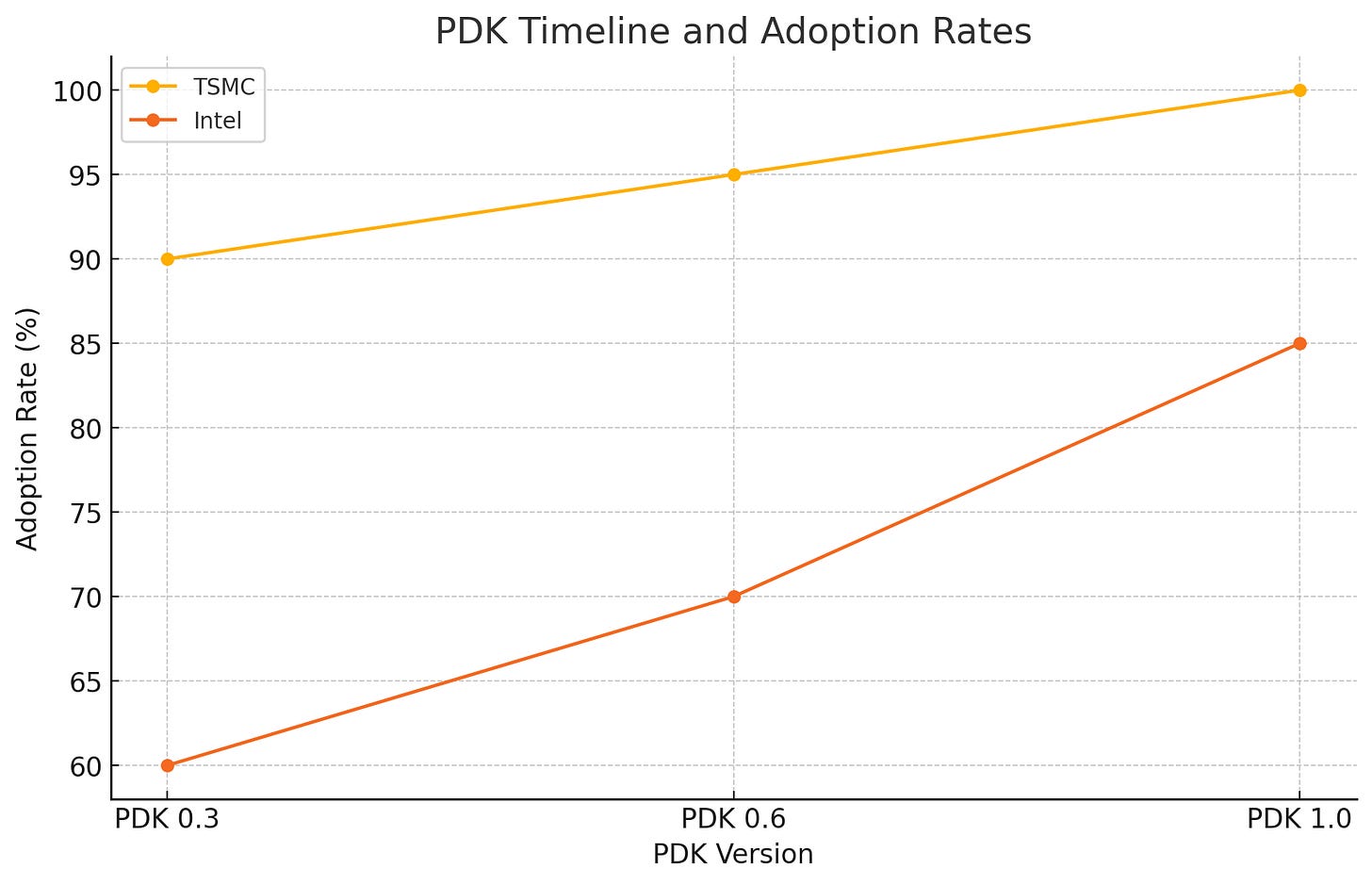
TSMC’s cadence in releasing PDKs is a benchmark for the industry:
PDK 0.3: Early access for feasibility studies.
PDK 0.6: Enhanced support for detailed design integration.
PDK 1.0: Full functionality to enable design tape-out.
Contrast this with Intel Foundry Services (IFS), where delays in PDK updates have frustrated potential customers, undermining its push to compete with TSMC.
TSMC’s ability to provide timely PDKs, co-develop IP libraries, and ensure seamless design tape-out enables customers to launch their products faster, giving them a significant time-to-market advantage.
Key Stat: Over 90% of fabless semiconductor companies globally rely on TSMC’s design ecosystem to bring their products to life
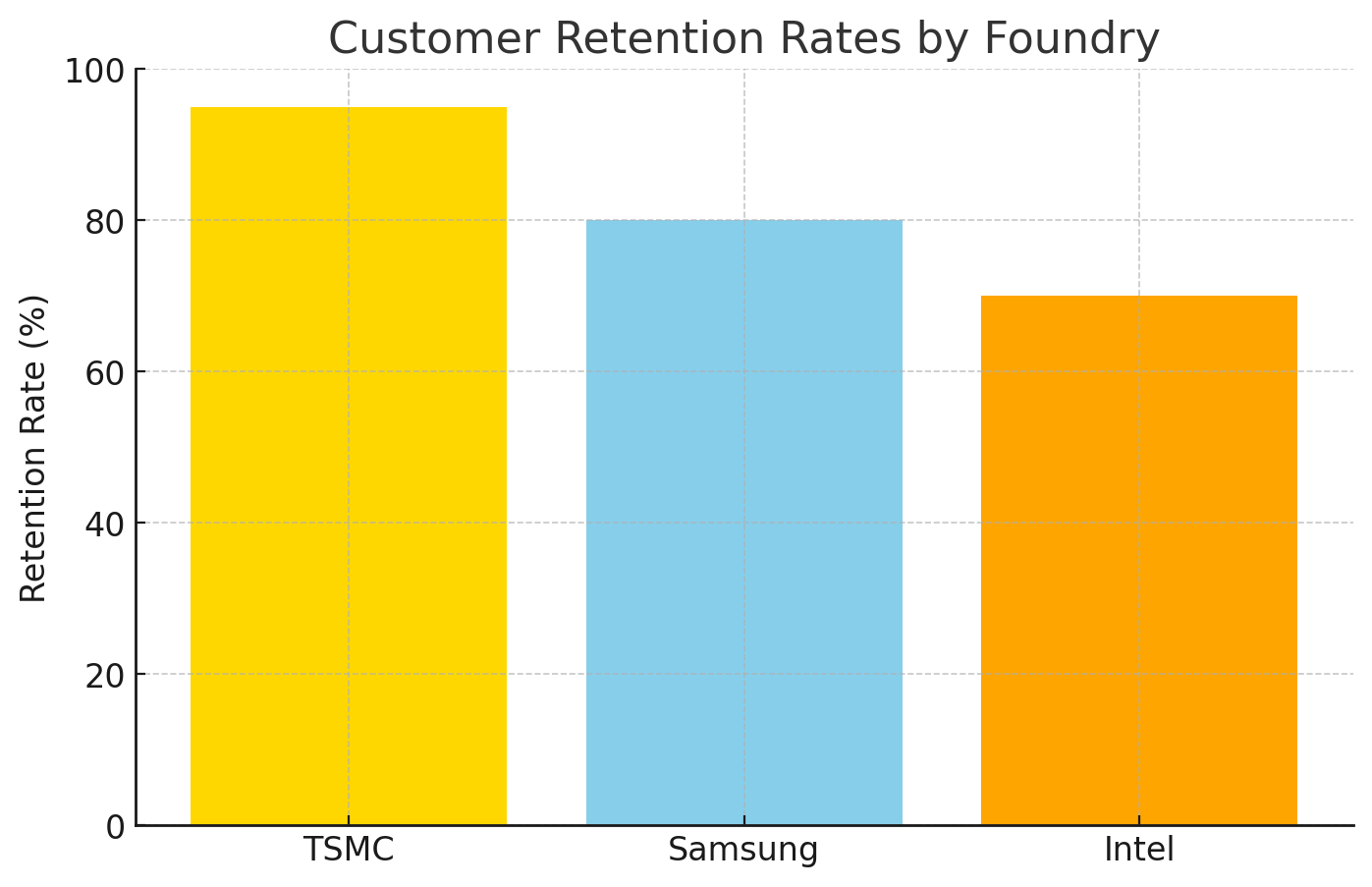
3. Trust: The Foundation of Long-Term Partnerships
At the heart of TSMC’s dominance lies something intangible but invaluable—trust. Customers view TSMC as more than just a foundry; they see it as a strategic partner committed to their success.
TSMC works closely with its customers to co-develop derivative technologies that fill gaps in legacy nodes. This not only keeps older fabs fully utilized but also strengthens its relationships with customers who rely on those nodes for mature products.
Samsung Foundry, on the other hand, has faced trust issues, from underwhelming yields at advanced nodes to perceived prioritization of its own products (like Exynos chips) over third-party customers.
Key Stat: TSMC’s customer retention rate exceeds 95%, underscoring its status as the most trusted name in the business.
4. Economies of Scale and High Barriers to Entry
The semiconductor foundry business is not for the faint of heart—it demands astronomical capital investments and precise execution. TSMC leads the industry with an R&D budget exceeding $7 billion in 2023, and each of its state-of-the-art fabs costs upwards of $20 billion. This scale of investment creates formidable barriers for competitors looking to enter or expand in the market.
TSMC’s fabs are not just costly—they are also massive. Their larger production volumes allow TSMC to achieve better economies of scale, translating into gross margins of 55.5% in Q3 2023, significantly higher than competitors like Samsung Foundry (38%) and Intel Foundry Services (35%).
By spreading costs across a broad customer base—including tech giants like Apple, NVIDIA, and AMD—TSMC keeps per-unit production costs low, reinforcing its competitive edge.
Stat: TSMC ships over 13 million wafers annually, serving 90% of the world’s leading fabless chipmakers, a scale no competitor comes close to matching.
Additionally, TSMC’s ability to spread costs across a wide customer base allows it to maintain lower per-unit production costs, a feat competitors struggle to replicate.
Conclusion
TSMC’s dominance in the foundry business is not accidental. It is the result of decades of technological leadership, strategic investments, and a customer-centric ecosystem. The barriers to entry in this industry are astronomical, and even the strongest competitors face an uphill battle.
As technology continues to evolve, TSMC’s ability to innovate, scale, and adapt ensures that its reign will remain unchallenged for the foreseeable future.
Let me know your thoughts in the comments! Are there other factors you believe could challenge TSMC’s throne, or do you think its dominance is inevitable?
In next post, I will discuss the strategy Intel and Samsung can employ to compete with TSMC.
Comments
Post a Comment